Healthy patient occurs from time to time:
PLAX focused on the left ventricular cavity

PLAX focused on the base of the heart
PLAX, CFM
Visualisation of diastolic flows: flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle (yellow arrow), flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle (green arrow) – here overlapping with the flow signal from LVOT due to slice thickness artefact (the source signal coming from the right side of the heart).

PSAX, at the level of the base of the heart
The aortic valve with three cusps.

PSAX, at the level of the ascending aorta and pulmonary artery

PSAX, at the level of the ascending aorta and pulmonary artery
Flow in the pulmonary artery. Aliasing is present around the aortic bulb (i.e. velocity at this place exceeds 63 cm/s).
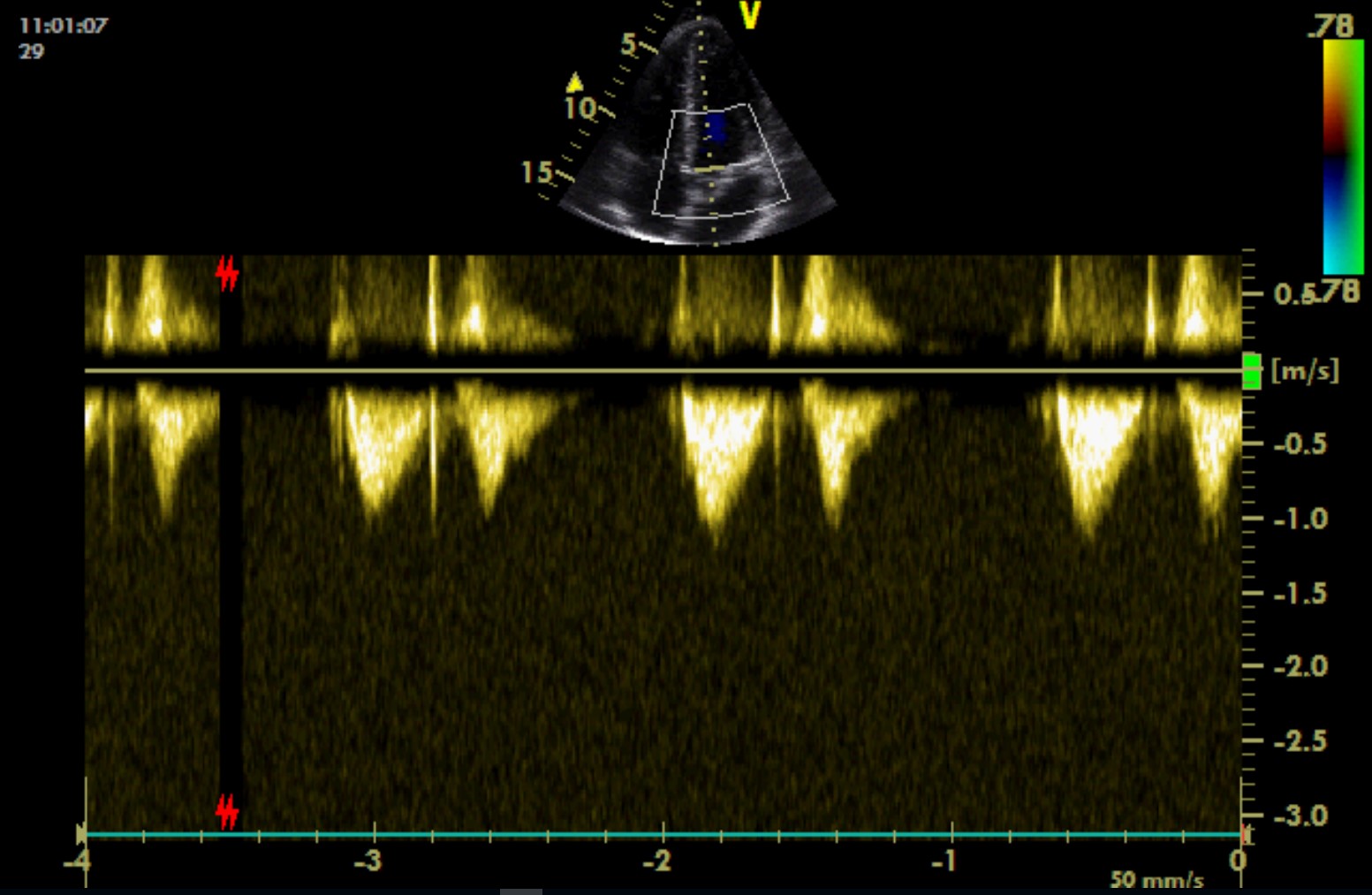
PSAX, at the level of ascending aorta and pulmonary artery, PW across RVOT / pulmonary artery
Symmetric flow curve in the pulmonary artery (type-I curve).

PSAX, at the level of ascending aorta and pulmonary artery, visualisation of the right side of the heart, CFM
Mild tricuspid regurgitation (pale blue colour).

PLAX-RV
Atypical projection. Right ventricular inflow tract below the probe, tricuspid valve and right atrium more deeply. The Eustachian valve at the ostium of inferior vena cava into the right atrium. Cranial parts of the right atrium with the ostium of superior vena cava are not visible.

PLAX-RV
Atypical projection. Right ventricular inflow tract below the probe, tricuspid valve and right atrium more deeply. An asymmetric jet of tricuspid regurgitation. Mild tricuspid regurgitation is physiological.
PSAX, at the level of ascending aorta and pulmonary artery, visualisation of the right side of the heart, CW line across the orifice of the tricuspid valve.
A pressure gradient of tricuspid regurgitation is minimal, no sign of pulmonary hypertension. Flow from inferior vena cava to right atrium in the direction of the probe is marked with the blue arrow.

PSAX, at the level of mitral valve

PSAX, at the level of papillary muscles

PSAX, at the level of heart apex

A4C

A4C/A5C, CFM.
Direction of flow during diastole.
A4C, CFM, CW line across the mitral valve
CW is used here atypically to assess flow across healthy mitral valve due to the fact, that the patient presents with hyperdynamic circulation and velocities exceed Nyquist limit of PW Doppler. A-wave mounts on E wave. Normal deceleration time. Considering also the morphology of the mitral valve, mitral stenosis can be excluded. Flow is accelerated due to a high flow volume (high stroke volume).
A4C, M mode
TAPSE
A4C, M mode
MAPSE

A5C
A5C, CW line across the aortic valve
Normal flow across the aortic valve. No aortic stenosis detected.

A2C

A3C

A3C, CFM
Visualisation of left ventricular systole with flow in direction of LVOT and aortic valve.